-

-

-

- HOME
- 연구동향
- MERRIC인
- 메릭웨비나
- 공학DB
- 문헌정보
- 기계로봇소식
- MERRIC은?
- 회원가입
- 로그인
| 지도교수 | 송철 |
|---|---|
| 전공분류 | 로봇공학(Robotics), |
| 주소 | 대구광역시 달성군 현풍면 테크노중앙대로 333 |
| 전화 | 053-785-6215 |
| 홈페이지 | https://ibomdgist.wordpress.com/ |
Welcome to IBOM lab!!
The research topics of IBOM lab are various biomedical applications based on human robot interaction, virtual reality, biomedical robotics, intelligent opto-mechatronics, biomedical imaging, neuro-rehabilitation, brain engineering, and so on. To solve many complex problems in engineering and science, smarter approaches in convergence research are required.
The key contribution of the research in IBOM lab is to give high impact of the systematic performance in biomedical applications by adapting new technology.
In IBOM lab, the members can be an all-round researcher who has enough background on AI mechatronics, robotic manipulator, optomechatronic system, software programming, ,…
Always welcome, and be with us!!
AI-based Clinical Decision Support System
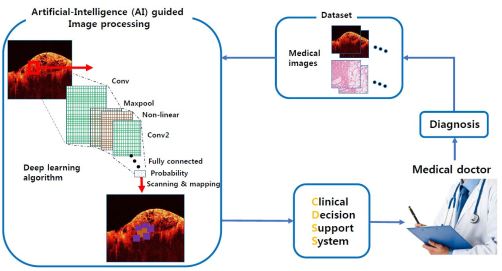
Purpose
Design a practical artificial intelligence-guided clinical decision support system (AI-CDSS), by using several deep learning methods such as transfer learning on convolutional neural network (CNN) or other network structures to classify disease models.
Contents
Recently, several image-based diagnostic methods assisted by machine learning has been reported, and some of them show great performance. Those methodologies will be utilized to make a practical AI-CDSS, enabling to extract crucial features that medical doctors couldn’t recognize. Here, we are developing AI-based CDSS platform. Various medical images can serve as an input data set, and superior training network structure will be further investigated.
AI-based Virtual Reality-Human Robot Interaction (HRI)

Contents
HRI is a field of study dedicated to understanding, designing, and evaluating robotic systems for use by or with humans. Interaction is communication between robot and human
Purpose
: Virtual reality (VR) technology has been highlighted recently in many industrial and biomedical fields. It has previously been applied to robotics micromanipulation, military skills in soldiers, phobia treatment, post-traumatic stress disorder, motor skill training on athletes, and surgical skill improvement. We research how to combine virtual reality technologies with human-robot interactions technologies. Since VR affords a more immersive experience than real environment, human robot interaction with VR can be used in training robotic surgery and remoting manipulator, which is safe and low-cost.
Virtual Reality
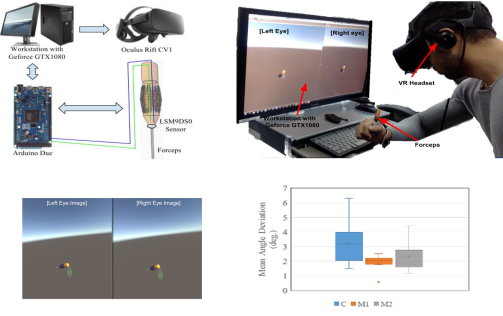
Visual Stimuli Modification in Virtual Reality
In the micro-surgical tasks, we assume that suppressing hand tremor is the first consideration to achieve successful surgery operation. We aim to assist a surgeon to have better self-awareness of hand tremor by modifying visual stimuli.
System Implementation
Here, it is presented two ways of visual stimuli modification using virtual reality: Modification 1: Tremor amplification and Modification 2: Object size magnification. By defining an orientation matching task, in which a subject is asked to match the orientation of virtual forceps to a given reference orientation. During the tasks, the subjects were instructed to put their elbow and lower arm on a table. For each trial, the subjects were requested to hold the forceps with the reference angle shown in the virtual reality screens (i.e., hologram image) for 20 seconds. The hologram reference image was in the same position and orientation throughout the tasks (yaw = 90º).
- John Prada, Taiwoo Park, Sunjin Jang, Jintaek Im, and Cheol Song, “Exploring the Potential of Modifying Visual Stimuli in Virtual Reality to Reduce Hand Tremor in Micromanipulation Tasks”, Current Optics and Photonics, Vol. 1, No. 6, pp. 642-648, 2017.12.25
Atmospheric Pressure Mass Spectrometry Imaging System
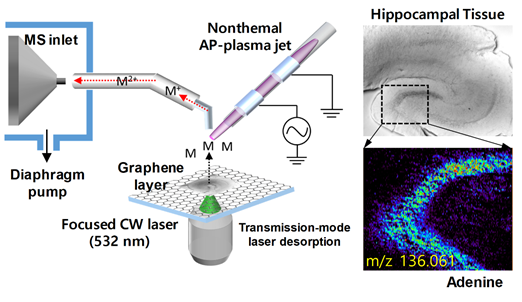
Purpose:
Development of novel atmospheric pressure mass spectrometry (AP-MS) imaging method based on nanomaterial-assisted (pulse/CW) laser desorption and subsequent non-thermal plasma induced ionization.
Efficient laser desorption techniques for bio-molecule sampling using nanomaterials (AuNPs/AgNps, Go/rGO nanosheets, carbon dots, and MoS2), graphene-layer substrate, and AuNP-layer substrate.
Content:
Atmospheric pressure mass spectrometry (AP-MS) imaging is a member of the mass spectrometry (MS) imaging family, in which ionization occurs at atmospheric pressure with the samples being analyzed in their native state. In ambient desorption/ionization, 1) the surface is sampled with minimal or no preparation, 2) ionization occurs externally to the mass spectrometer, and 3) ion, not the entire sample, are introduced into the mass spectrometer.
The AP-MS imaging system with an efficient desorption procedure using focused lasers with an aid of nanomaterials and a subsequent AP-plasma ionization step shows detailed chemical information of biological tissue with micrometer spatial resolution.
The transmission-mode laser configuration provides precise desorption performance to facilitate MS imaging. The transmission-mode laser configuration and the use of nanomaterial-coated substrates show greatly improved laser desorption performance, and the desorbed biomolecules inevitably meet the atmospheric pressure helium plasma medium, resulting in AP-MS imaging.
- Jae Young Kim, Sun Young Lee, Dae Won Moon, Ji-Won Park, Dong-Kwon Lim, and Cheol Song, “Atmospheric pressure mass spectrometric imaging of bio-tissue specimen using electrospray-assisted CW laser desorption and ionization source,” Biointerphases, Vol.14 No.4, pp.041001-1~7, 2019.07.26
- Jae Young Kim, Heejin Lim, Sun Young Lee, Cheol Song, JiWon Park, Hyeon Ho Shin, Dong-Kwon Lim, and Dae Won Moon, “Graphene-Coated Glass Substrate for Continuous Wave Laser Desorption and Atmospheric Pressure Mass Spectrometric Imaging of Live Hippocampal Tissue”, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Vol. 11, , pp.27153-27161, 2019.06.11
Microsurgical Robot
Purpose
: Humans have some degree of hand tremor ranging from not noticeable in everyday tasks, to incapacitating tremor due to various neurodegenerative conditions.
: All surgeons strive to minimize tremor to successfully complete microsurgical procedures.
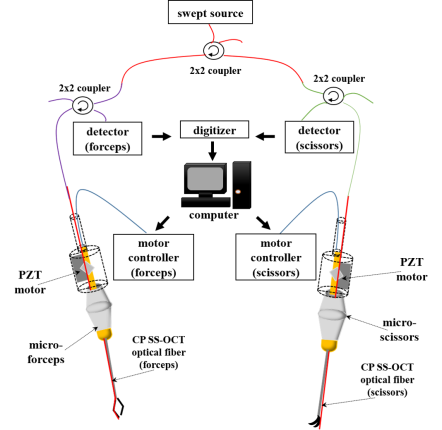
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
: Optical coherence tomography has emerged as a dominant diagnostic imaging modality in clinical ophthalmology
: OCT can also be used as very precise distance sensor with high speed in biological applications, compared to other range-finding techniques such as ultrasound imaging or MRI.
Robot aided tool
: contains precise motor control to achieve surgical objectives and minimize surgical risks.
- Dongwoo Koo, Hyun-Cheol Park, Peter L. Gehlbach, and Cheol Song, “Development and preliminary results of bimanual smart micro-surgical system using a ball-lens coupled OCT distance sensor”, Biomedical Optics Express, Vol.7, No.11, pp.4816-4826, 2016.10.31.
- Chaebeom Yeo, Hyun-cheol Park, Seon-jin Jang, Peter L. Gehlbach, and Cheol Song, “Dual optical coherence tomography sensor guided, two-motor, horizontal SMART micro-scissors”, Optics Letters, Vol.41, No.20, pp.4723-4726, 2016.10.10.
Multi-Degree-Of-Freedom Manipulator
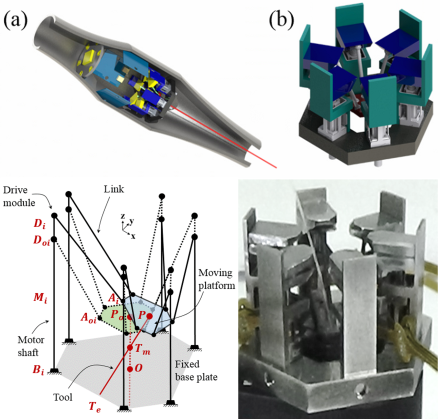
Surgical Limitations of Micro-Surgery
– Physiological hand tremor about 6-12 Hz and 100 𝜇𝑚 motion
– Narrow eyesight
– Small size target
– Insufficient force feed back
Purpose
Multi DOF manipulator which can transfer the end-effector to any direction and orientation is needed to compensate the physiological hand tremor and overcome surgical limitations
Parallel Manipulator
LINAPOD platform is a kind of 6 DOF parallel manipulator. This platform with very high stiffness employs drive modules and linear drives for linear motion. And the LINAPOD platform is used to develop robot-assisted handheld manipulator for microsurgery
- Dongwoo Koo and Cheol Song: “Microsurgical Manipulator using a LINAPOD Parallel Mechanism”, HSMR 2016, London United Kingdom, Proceedings of HSMR pp.74-75, Jun. 27, 2016.
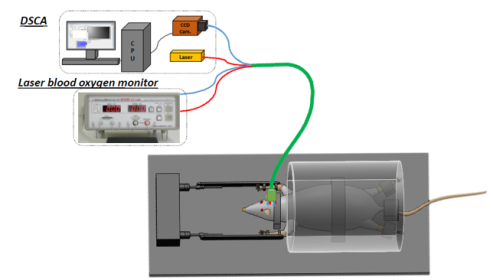
DSCA
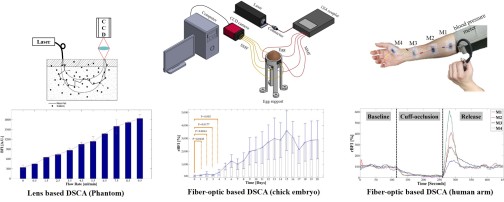
Diffuse Speckle Contrast Analysis (DSCA)
In human health, stable blood circulation is very important for transporting nutrition, maintaining the temperature, and preserving cell-level metabolism. Diffuse speckle contrast analysis (DSCA) is in-vivo multi-channel blood flow measurement system with simple data analysis, flexibility, and fast measurement speed. This system estimates blood flow index (BFI) dependent on the correlation of speckle pattern caused by blood flow.
Lens based DSCA
In experimental setup, a laser source (Near Infrared) is connected with multi-mode fiber. A CCD camera mounted with biconvex lens (Magnitude=1)
Fiber-optic based DSCA
The laser fiber is coupled with a 1×4 coupler. Four optical fibers as detection channels are closely placed in front of the CCD chip in a CCD camera.
The system performance is evaluated using a phantom which is similar to optical properties of human skin. As the flow velocity from a syringe pump increases, the BFI shows increasingly larger value. Also, the DSCA system is applied to blood flow measurement on both human arm and chick embryos. In human arm experiment, the protocol has three periods including baseline, cuff-occlusion, and release, controlled by a blood pressure meter. At different periods, the BFI dramatically decreases and increases corresponding to the blood flow. In the chick embryo experiment, the BFI is measured during incubation period of chick embryos. As the embryo develops, the BFI gradually increases. In addition, the DSCA could determine the vital sign of the embryos. In conclusion, the DSCA system could secure in-vivo measurement of blood flow in deep tissues.
- Myeongsu Seong, Zephaniah Phillips V, Chaebeom Yeo, Cheol Song, Kijoon Lee, and Jae Gwan Kim, “Simultaneous blood flow and blood oxygenation measurements using a combination of diffuse speckle contrast analysis and near-infrared spectroscopy”, Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol.21, No.2, pp.027001, 2016.2.14
- Chaebeom Yeo, Hyun-cheol Park, Kijoon Lee, and Cheol Song, “Avian Embryo Monitoring during Incubation using Multi-channel Diffuse Speckle Contrast Analysis”, Biomedical Optics Express, Vol.7, No.1, pp.93-98, 2015.12.14 (Highlights on OSA(Optical Society of America) newsroom, Business Wire, Kyunghyang)
OCE System
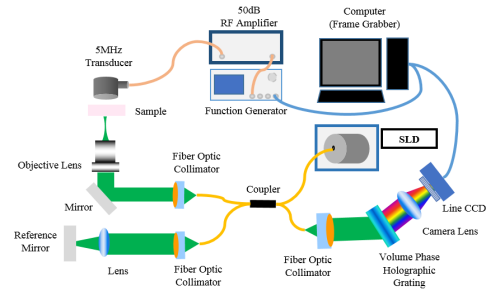
Biomechanics/Elasticity
Mechanical properties measurement is useful for studying change or characteristics of biological system like cell or tissues. Elasticity is one of major biomechanical properties. For examples elastic properties of cancer cell are related to metastasis of cancer cell and diseased cell’s elasticity is changed.
Elastography/OCE
Elastography is the method for measuring and imaging elasticity of sample by using various existing imaging modalities. OCE is one kind of elastography based on OCT system. While some force is applied to the surface of sample, OCT system measure and imaging surface displacement. From force and displacement information given by OCE system, Young’s modulus, signifying elasticity, is calculated.
Ultrasonic force
Ultrasound is used in a lot of biomedical field because of its safety. In OCE system, ultrasonic force is used to give a force to the sample surface.
- Yeonhee Chang, Jihun Kim, Jae Youn Hwang, Yongseok Oh, and Cheol Song: “Optical coherence elastogram of mouse cerebral cortex”, SfN 2016, San Diego United States, Proceedings of SfN, p.75, Nov. 16, 2016.
Neuro-rehabilitation
MCAO Surgery
From the artery occlusion surgery, ischemic rat model would be used for stroke rehabilitation study.
Blood oxygenation/flow monitoring
By using modified Beer-Lambert law and scattering effect, non-invasive laser blood monitoring is available to distinguish stroke state.
Normally infarcted area indicates hypoxia symptoms than non-infarcted area.
Blood flow is also slower in infarcted area.
Designs optimal gait-training for better recovery of stroke
From the novel quantitative and non-invasive recovery level analyses,
we could modulate training intensity to get optimized training effect.
- Chaebeom Yeo, Heejaung Kim, and Cheol Song, “Cerebral Blood Flow Monitoring by Diffuse Speckle Contrast Analysis during MCAO Surgery in the Rat”, Current Optics and Photonics, Vol. 1, No. 5, pp. 433-439, 2017.10.25.
Precision Actuation and Sensing System

Purpose
Determine number of turns of coil and thickness of leaf spring satisfying requirements of natural frequency and range which are given differently. Optimize voice coil motor system with other components such as driver, Dspace controller and capacitive sensor and check performance.
Stent
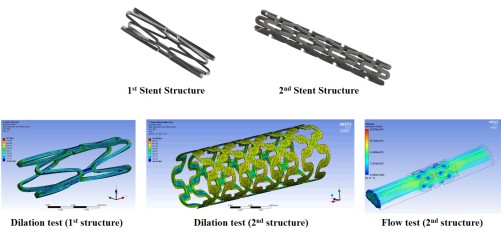
Microscale stent for rodent vasculature
Stent is frequently used to recover human vascular disease. The common stent for human has been developed. And, the development of stent for animal model is mostly focused on larger animals such as pig and rabbits. The rodent model has various advantages, involving economical approach, available to many genetic strains, and so on. We develop micro-scale stent for rodent with stable stent structure. To evaluate the structure, we observe the simulation depending on dilation, deflection, blood flow, as shown below figures. All simulation are tested using ANSYS software program. Then, the stents are practically validated on the rodents. Simultaneously, we apply assessment systems developed in our laboratory in order to monitor stent performance.
Atmospheric pressure mass spectrometric imaging of bio-tissue specimen using electrospray-assisted CW laser desorption and ionization source,
Biointerphases, 2019-07, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 41001~ 0
John Prada, Taiwoo Park, Sunjin Jang, Jintaek Im, and Cheol Song
Exploring the Potential of Modifying Visual Stimuli in Virtual Reality to Reduce Hand Tremor in Micromanipulation Tasks
Current Optics and Photonics, 2017-12, Vol. 1, No. 6, pp. 642~ 648
Jae Young Kim, Heejin Lim, Sun Young Lee, Cheol Song, JiWon Park, Hyeon Ho Shin, Dong-Kwon Lim, and Dae Won Moon
Graphene-Coated Glass Substrate for Continuous Wave Laser Desorption and Atmospheric Pressure Mass Spectrometric Imaging of Live Hippocampal Tissue
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019-06, Vol. 11, No. 0, pp. 27153~ 27161
















